Roger Luebeck © 2008, 2011, 2024
The preprint of my journal article is at this link: preprint.special_relativity.pdf
Also see my tutorial for computing non-kinematical and kinematical time-keeping dilation, with commentary on the Hafele-Keating study of circumnavigating jets: time-dilation.pdf
In as few words as possible:
The absolute approach to relativity reveals the same thing that the relative approach assumes -- that there is no privileged frame of reference in which to conduct experiments. Thus, the absolutist and the relativist agree that one cannot detect one's motion status relative to the universe using electromagnetic experimentation.
It is meaningless to ascribe linear or rotational motion to the whole of the universe, considering that the universe has nothing to push off against. It is the baseline for the motion of its constituent parts.
A constituent part -- such as a clock -- cannot impart inertial properties (beyond and infinitesimal) to the universe. Thus, the universe is the imparter of inertial properties and is the absolute frame of reference.
The fact that energy and matter can be converted to each other, along with the fact that a photon exists as pure energy, tells us that light has an unvarying speed -- when free of gravitational influence -- and is also the limiting speed.
All processes are constrained by the speed of light. Therefore, kinematical clock functioning (time-keeping) of every nature is dependent on the speed of light, at even the atomic level.
The person that changes his inertial motion to facilitate a reunion with another person is the one that records the lesser amount of time over the interval in which they were apart. He is the one who would experience the force of acceleration associated with reversal of motion.
Acceleration implies an initial and final state of inertial motion -- necessarily different from each other in an actual sense for the very reason that acceleration is actual. It is not the acceleration itself that generates the time-keeping differential; rather, it is the difference in actual speed between the two persons in conjunction with distance covered in absolute terms by both persons.
The two persons cannot both have recorded less time than the other. This proves that totality (the universe) is the imparter of inertial properties and is the judge of motion.
The math is precisely correct when the acceleration portion is eliminated by virtue of transfer of clock information across inertial frames between an outbound person and an inbound person and there is then a subsequent comparing of total clock-times for all parties involved.
A satellite orbiting the earth has a greater speed relative to totality -- and to every constituent part of totality -- than does a station on the surface of the earth. Try to imagine otherwise. After allowing for the non-kinematical (general relativity) clock-rate difference between a clock on the surface of the earth and a clock on a satellite, we find that the clock on the satellite records less kinematical time than the earth-surface clock over a given interval. This proves, even more simply, that there is a hierarchy of kinematical clock-rates, dependent on a hierarchy of inertial motion.
Since a photon has a non-zero amount of momentum, a moving source of emission will affect the vector components of its path despite the fact that it cannot affect its speed. The equation for kinematical time-keeping is simply derived by way of a two-dimensional study of a photon clock:
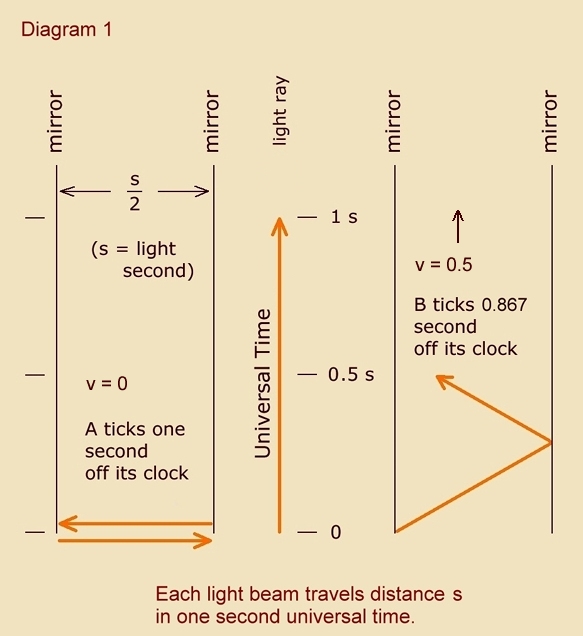
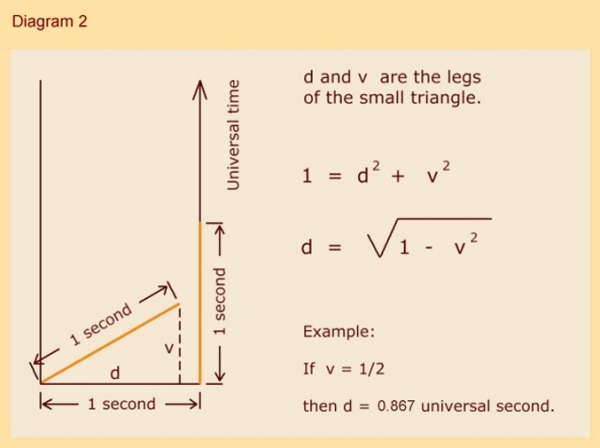
If you could travel at the speed of light (you would need to be impossibly massless), you could cross the universe with no sense of time having passed, as there would be no possibility of registering a tick on your clock (your aging). That is why we can say that from the perspective of light, light is everywhere at once.
The consideration that synchronization is vital for the stability of atoms, and that all processes (including the communication of force) are constrained by the speed of light, leads directly to length contraction for rigid bodies and for the spatial separation of objects in the same inertial frame. These relationships are communicated by the absolute nature of light (broadly -- energy).
(Energy itself is the ultimate absolute frame of reference, from my point of view. From my point of view, it is what matter is born of. This might sound contrary to the current standard model of quantum mechanics with its fundamental particles of matter, which are simply regarded as possessing an energy equivalence. I regard such fundamental particles of matter as possessing directionless energy. It's a slightly different -- yet compatible -- perspective with slightly different terminology. The "directionless" energy can be thought of as "multi-directed" energy -- as opposed to kinetic energy -- to enable a natural derivation of E = m c^2, which I have done.)
The relationship between photons and the all-encompassing energy behind totality is a mystery. (I like to think of photons as itty bitty angels -- agents for the all-encompassing energy (almighty god) behind totality. But don't try to extend that analogy.)
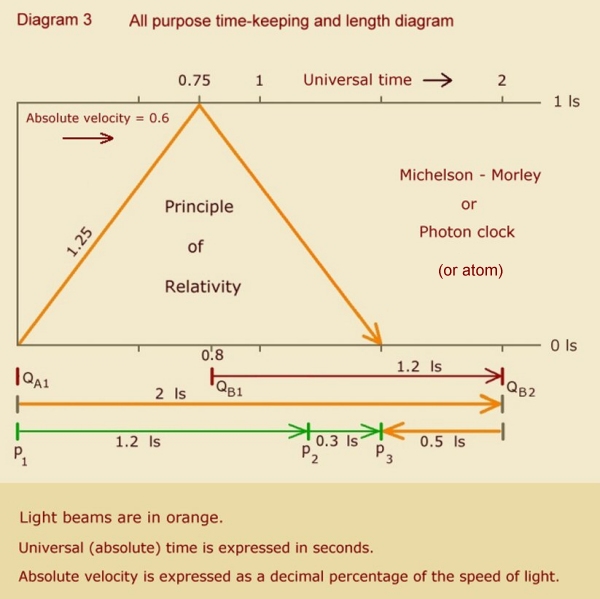
It is no coincidence that length is contracted to the same degree as time-keeping. And this sameness of contraction gives us symmetry of measure across inertial frames, as well as consistent measure of light speed -- regardless of inertial frame.
That length is contracted to the same degree as time-keeping is proved with the use of the following diagrams and simple algebra:

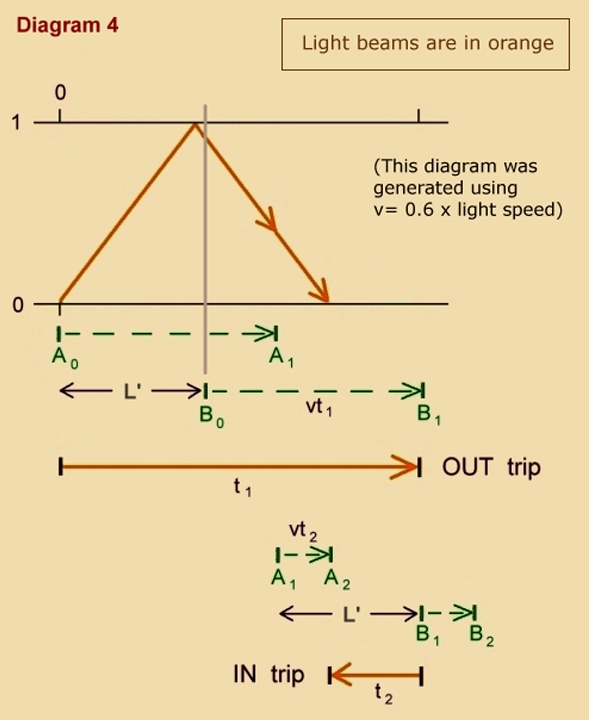

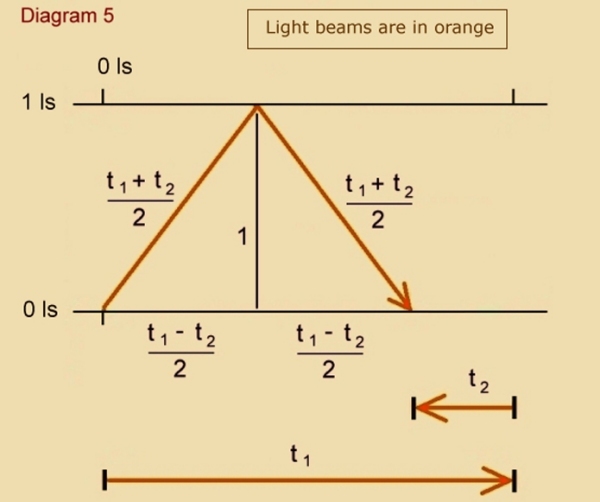
Finally, note that we do not need the spacetime model to precisely derive the non-kinematical clock-slowing caused by actual gravitational force:
When Newton's law of gravity is combined with the equivalence principle and the simple kinematical clock-slowing of uniform motion, the resulting set of equations precisely match Einstein's treatment for gravitational clock-slowing associated with an actual gravitational force (versus an actual gravitational force plus a gravitational effective force); that is, the actual gravitational force of a non-rotating massive body versus the actual plus effective force of a rotating massive body.
Below: Newton's law of gravity dictates the slowing of light. That, in conjunction with kinematical clock-rate slowing, yields the total clock-rate slowing.
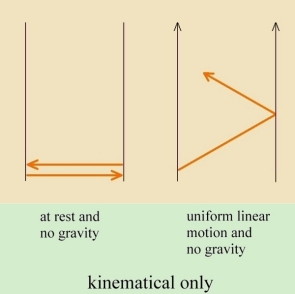
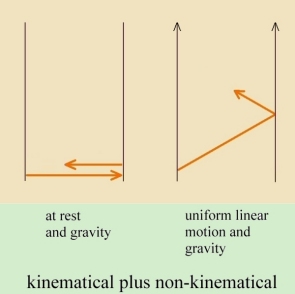
For a discussion of how Newton's law of gravity -- in combination with the speed of light (absolute nature of light) and the equivalence principle -- could suffice to explain all gravitational effects, bringing it into agreement with experiments (such as planetary precession and bending of starlight), see: spacetime curvature
For diagrams and equations demonstrating symmetry of measure, see:
preprint.special_relativity.pdf
A twins paradox adventure is also diagrammed and algebraically analyzed in the article linked to above. Consistent light-speed measure, independent of inertial frame, is diagrammed in my book -- along with all other diagrams and analyses.
© 2008, 2011, 2024 Roger Luebeck
Updated 12/29/2025
site map
The preprint of my journal article is at this link: preprint.special_relativity.pdf
Also see my tutorial for computing non-kinematical and kinematical time-keeping dilation, with commentary on the Hafele-Keating study of circumnavigating jets: time-dilation.pdf
In as few words as possible:
The absolute approach to relativity reveals the same thing that the relative approach assumes -- that there is no privileged frame of reference in which to conduct experiments. Thus, the absolutist and the relativist agree that one cannot detect one's motion status relative to the universe using electromagnetic experimentation.
It is meaningless to ascribe linear or rotational motion to the whole of the universe, considering that the universe has nothing to push off against. It is the baseline for the motion of its constituent parts.
A constituent part -- such as a clock -- cannot impart inertial properties (beyond and infinitesimal) to the universe. Thus, the universe is the imparter of inertial properties and is the absolute frame of reference.
The fact that energy and matter can be converted to each other, along with the fact that a photon exists as pure energy, tells us that light has an unvarying speed -- when free of gravitational influence -- and is also the limiting speed.
All processes are constrained by the speed of light. Therefore, kinematical clock functioning (time-keeping) of every nature is dependent on the speed of light, at even the atomic level.
The person that changes his inertial motion to facilitate a reunion with another person is the one that records the lesser amount of time over the interval in which they were apart. He is the one who would experience the force of acceleration associated with reversal of motion.
Acceleration implies an initial and final state of inertial motion -- necessarily different from each other in an actual sense for the very reason that acceleration is actual. It is not the acceleration itself that generates the time-keeping differential; rather, it is the difference in actual speed between the two persons in conjunction with distance covered in absolute terms by both persons.
The two persons cannot both have recorded less time than the other. This proves that totality (the universe) is the imparter of inertial properties and is the judge of motion.
The math is precisely correct when the acceleration portion is eliminated by virtue of transfer of clock information across inertial frames between an outbound person and an inbound person and there is then a subsequent comparing of total clock-times for all parties involved.
A satellite orbiting the earth has a greater speed relative to totality -- and to every constituent part of totality -- than does a station on the surface of the earth. Try to imagine otherwise. After allowing for the non-kinematical (general relativity) clock-rate difference between a clock on the surface of the earth and a clock on a satellite, we find that the clock on the satellite records less kinematical time than the earth-surface clock over a given interval. This proves, even more simply, that there is a hierarchy of kinematical clock-rates, dependent on a hierarchy of inertial motion.
Since a photon has a non-zero amount of momentum, a moving source of emission will affect the vector components of its path despite the fact that it cannot affect its speed. The equation for kinematical time-keeping is simply derived by way of a two-dimensional study of a photon clock:


If you could travel at the speed of light (you would need to be impossibly massless), you could cross the universe with no sense of time having passed, as there would be no possibility of registering a tick on your clock (your aging). That is why we can say that from the perspective of light, light is everywhere at once.
The consideration that synchronization is vital for the stability of atoms, and that all processes (including the communication of force) are constrained by the speed of light, leads directly to length contraction for rigid bodies and for the spatial separation of objects in the same inertial frame. These relationships are communicated by the absolute nature of light (broadly -- energy).
(Energy itself is the ultimate absolute frame of reference, from my point of view. From my point of view, it is what matter is born of. This might sound contrary to the current standard model of quantum mechanics with its fundamental particles of matter, which are simply regarded as possessing an energy equivalence. I regard such fundamental particles of matter as possessing directionless energy. It's a slightly different -- yet compatible -- perspective with slightly different terminology. The "directionless" energy can be thought of as "multi-directed" energy -- as opposed to kinetic energy -- to enable a natural derivation of E = m c^2, which I have done.)
The relationship between photons and the all-encompassing energy behind totality is a mystery. (I like to think of photons as itty bitty angels -- agents for the all-encompassing energy (almighty god) behind totality. But don't try to extend that analogy.)

It is no coincidence that length is contracted to the same degree as time-keeping. And this sameness of contraction gives us symmetry of measure across inertial frames, as well as consistent measure of light speed -- regardless of inertial frame.
That length is contracted to the same degree as time-keeping is proved with the use of the following diagrams and simple algebra:




Finally, note that we do not need the spacetime model to precisely derive the non-kinematical clock-slowing caused by actual gravitational force:
When Newton's law of gravity is combined with the equivalence principle and the simple kinematical clock-slowing of uniform motion, the resulting set of equations precisely match Einstein's treatment for gravitational clock-slowing associated with an actual gravitational force (versus an actual gravitational force plus a gravitational effective force); that is, the actual gravitational force of a non-rotating massive body versus the actual plus effective force of a rotating massive body.
Below: Newton's law of gravity dictates the slowing of light. That, in conjunction with kinematical clock-rate slowing, yields the total clock-rate slowing.


For a discussion of how Newton's law of gravity -- in combination with the speed of light (absolute nature of light) and the equivalence principle -- could suffice to explain all gravitational effects, bringing it into agreement with experiments (such as planetary precession and bending of starlight), see: spacetime curvature
For diagrams and equations demonstrating symmetry of measure, see:
preprint.special_relativity.pdf
A twins paradox adventure is also diagrammed and algebraically analyzed in the article linked to above. Consistent light-speed measure, independent of inertial frame, is diagrammed in my book -- along with all other diagrams and analyses.
© 2008, 2011, 2024 Roger Luebeck
Updated 12/29/2025
site map